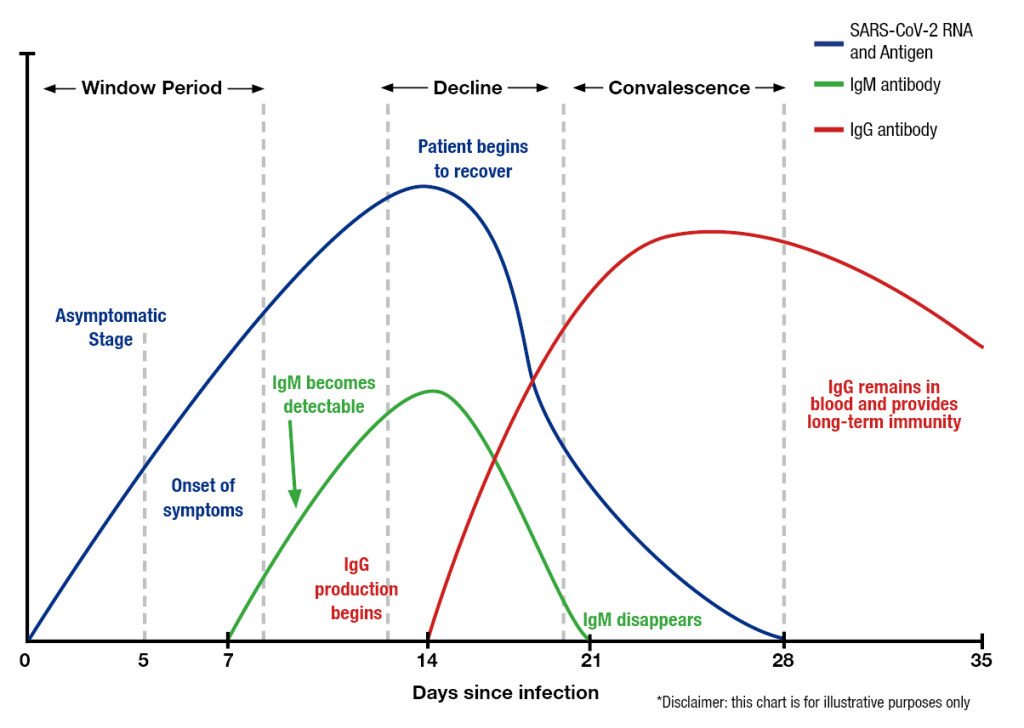
What are Monoclonal Antibodies?
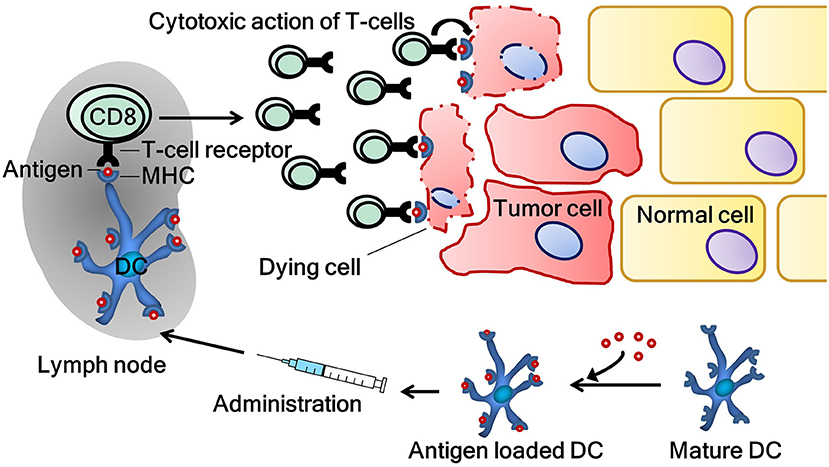
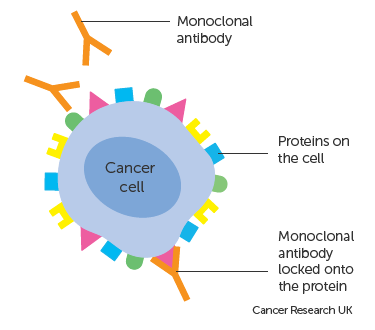
According to this article by the manufacturers of Rituximab, or the brand name of Rituxan, this prescription drug is used to treat adults with Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. This medicine works through monoclonal antibodies which are proteins that attach to antigens (or foreign substances in the body) and mark them for the immune system to kill them or cells infected with them. Monoclonal antibodies in particular are made in labs to target a specific antigen, and make copies of it by fusing B cells (capable of making antibodies) and myeloma cells (which grow indefinitely). Different monoclonal antibodies are made using different combinations of mouse/rat and human proteins. They collect these proteins by extracting spleen cells from the subject.
More About Rituximab
According to this article in medicinenet.com, Rituximab targets CD20, which is a receptor on almost all non-Hodgkins Lymphoma cells. The antibodies initiate lysis (disintegration) of these tumor cells when they attach. It can also prevent the growth of more tumor cells in some non-Hodgkins Lymphomas. This will then result in the killing tumor cells and hopefully remission for the patient when in combination with chemotherapy medicines. The drug will effect the acquired immune response of patients by depleting the numbers of B cells in lymph nodes and circulating through the blood. You could therefore say that this dug negatively affects the immune system, and that too much of the drug can lead to serious complications related to the lack of immune response.

More Information on the Medicine
Side effects of taking Rituximab include:
- Infusion related reactions (such as hives, itching, swelling, weakness, dizziness, etc. )
- Severe Infections
- Fatigue
- Body aches
- Runny nose
- Difficulty breathing
- Flushing
- Decreased blood pressure
- Tiredness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Aching joints hours after infusions
- More frequent upper respiratory tract infections
- Severe skin and mouth reactions (ulcers, peeling skin, blisters)
- Hepatitis B reactivation
- Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome (leading to kidney failure or abnormal heart rhythm)
- Heart Problems
- Kidney Problems
- Stomach and serious bowel problems
However, according to his article, this drug is commonly used to treat B-cell non-Hodgkins Lymphoma which has side effects which may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Coughing
- Chest Pain
- Trouble Breathing
- Fever
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night Sweats
- Persistant fatigue
As listed in the list of side effects for taking Rituximab, one of the complications includes Hepatitis B virus reactivation. According to this article in the World Journal of Hepatology, this can occur because the medicine is depleting B cells with CD20 and therefore immune globulin production which accelerates Hepatitis B replication. Furthermore, the effect on T cells that Rituximab has will further exacerbate liver problems with Hepatitis B.